Bayesian model averaging for logistic regression: Evaluating shooting skills of soccer players
Vienna University of Economics and Business
Nov 22, 2024
Motivation
How can evaluate the shooting skills of a soccer player?
Count how many goals a player scored during a season.
- Problem: Scoring highly depends on the circumstances of each shot.
- Solution: xG models \(\Rightarrow\) model success probability dependent on various important factor.
Count xG generated from shots and compare to actual goals (in a season).
- Problem: No stability, no uncertainty quantification.
Idea: Test whether player significantly impacts outcome of a shot.
Data
Event Stream Data:
- All shots (and other actions) from 5 Big European leagues from 2015/16 season
- 45198 shots (4308 resulted in goals, i.e. ~10%)
Features for each shot:
- 21 Explanatory variables (shot distance, shot angle, distances to defenders and goalkeepers,…)
- Outcome variable (shot result: goal/no goal)
- For each shot: shooter is known (~ 1000 distinct players took a shot in our data).
Data
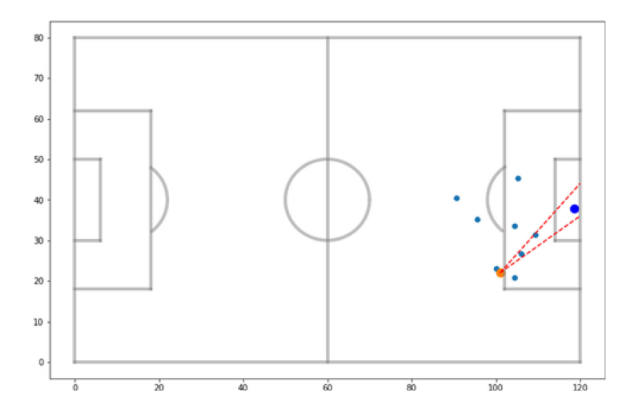
Hewitt and Karakuş (2023)
Methodology
Goal: Infer effect of a specific player on the outcome of a shot
Naive approach: Fit GLM (logistic regression) including all players and other features and use classical Wald tests.
- Problem: High dimensionality (more than 1000 players), sparsity and model misspecification.
What about fitting many small models with only one player:
- Problem: Non-collapsibility(model misspecification).
Question: How does Bayesian model averaging perform?
- How does the high-dimensionality affect the problem?
- Is non-collapsibility still a problem?
Side note: In a current project we use algorithm (i.e. model) agnostic conditional independence tests (COMETs) for this problem.
- Test the null hypothesis that \(Y\) (shot outcome) is independent of \(X\) (player involved) given \(Z\) (other shot specific features).
A primer on non-collapsibility
Logistic regression setup:
\[Y = I_{\{X + Z + L + \epsilon > 0\}}, \quad \epsilon \sim \text{logistic(0,1)}.\] \(X,Z,\) and \(L\) independent. But all of them influence outcome variable.
Consinder fitting two GLMs (both misspecified):
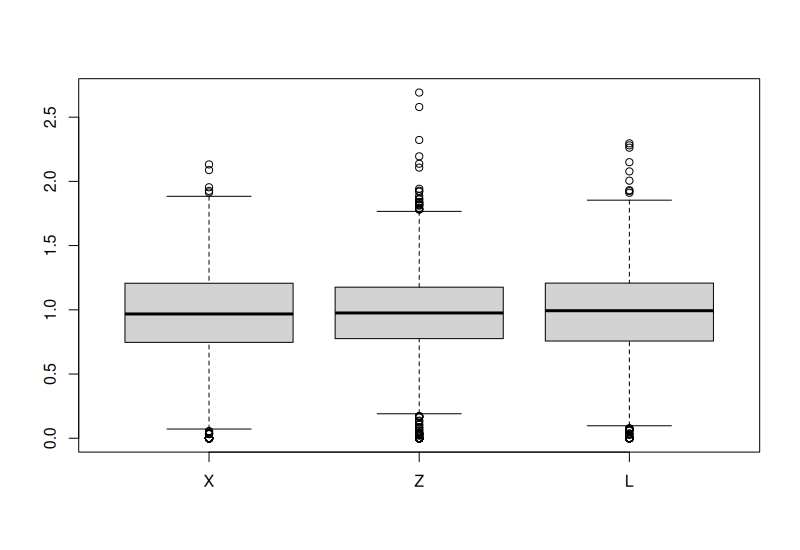
\(m_1:\) \[\log(\frac{\pi(X)}{1-\pi(X)}) = \beta_1 X\]
\(m_2:\) \[\log(\frac{\pi(X,Z)}{1-\pi(X,Z)}) = \beta_1 X + \beta_2 Z\]
A primer on non-collapsibility
Estimate for \(\beta_1\) in 1000 simulations (\(m_3\) is correct model):
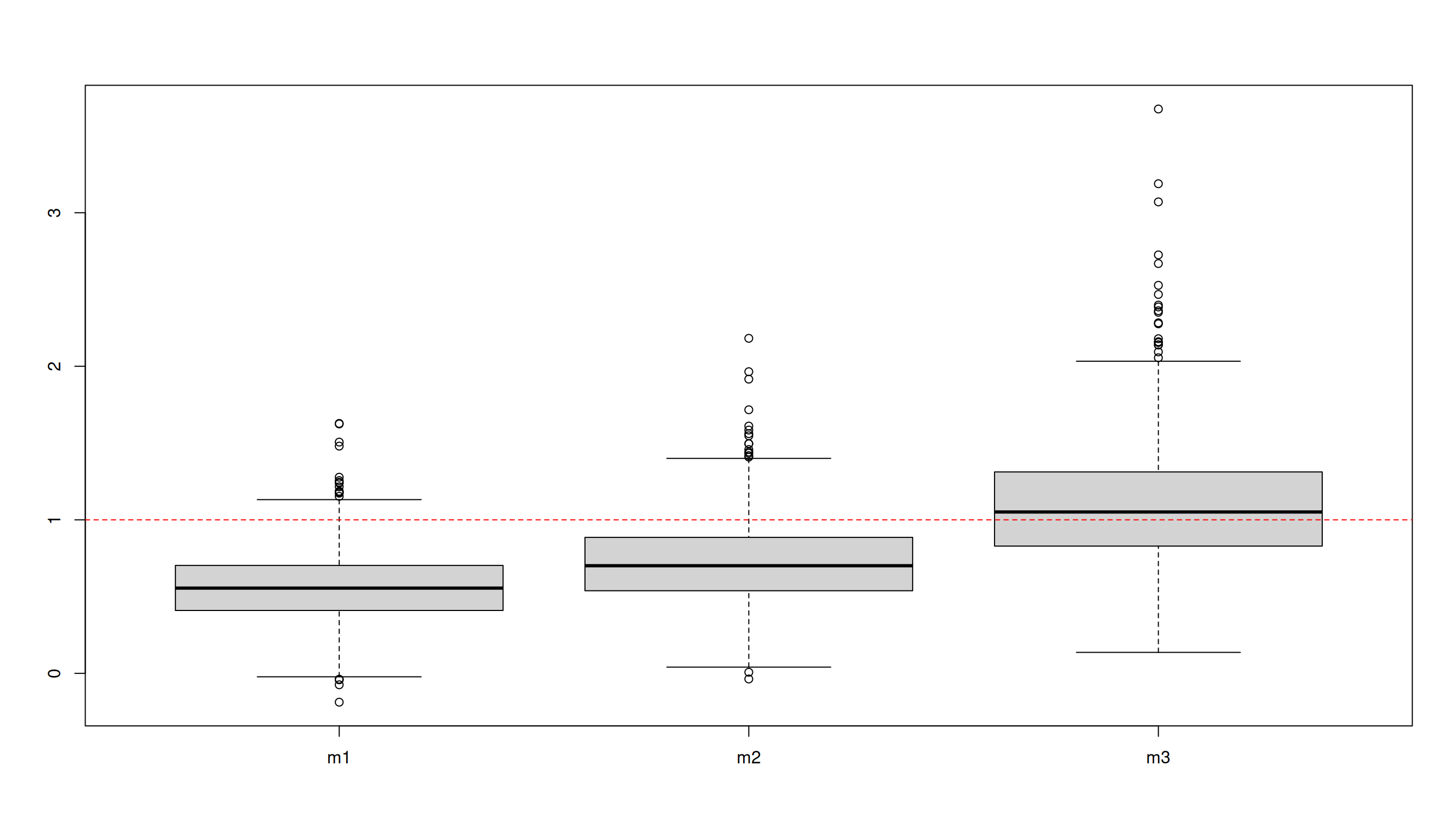
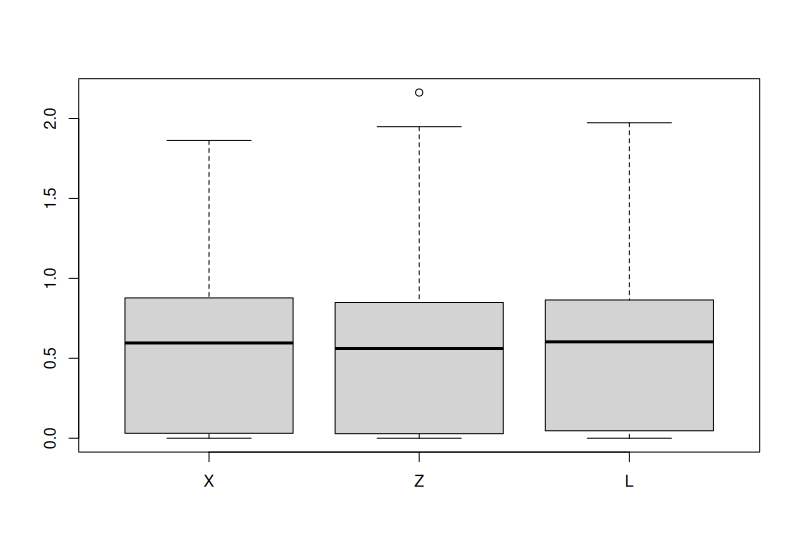
Linear model comparison
As comparison: \(Y = X + Z + L - L_1 + \epsilon, \quad \epsilon \sim \text{N(0,1)}.\)
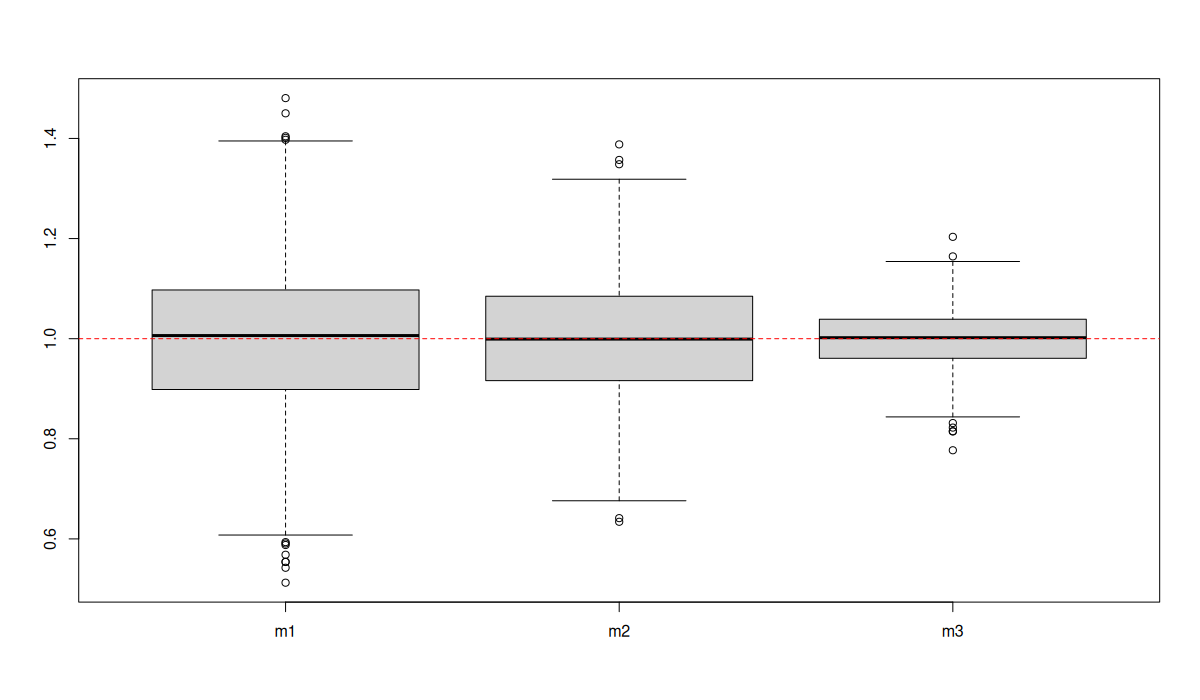
Non-collapsibility in BMA??
Logistic regression setup:
\[Y = I_{\{X + Z + L - L_1 + \epsilon > 0\}}, \quad \epsilon \sim \text{logistic(0,1)}.\] \(X,Z,L,\) and \(L_1\) independent. But all of them influence outcome variable. Furthermore 11 noise (irrelevant) variables in data. Total: 15 regressors (4 of them relevant).
Compare two cases:
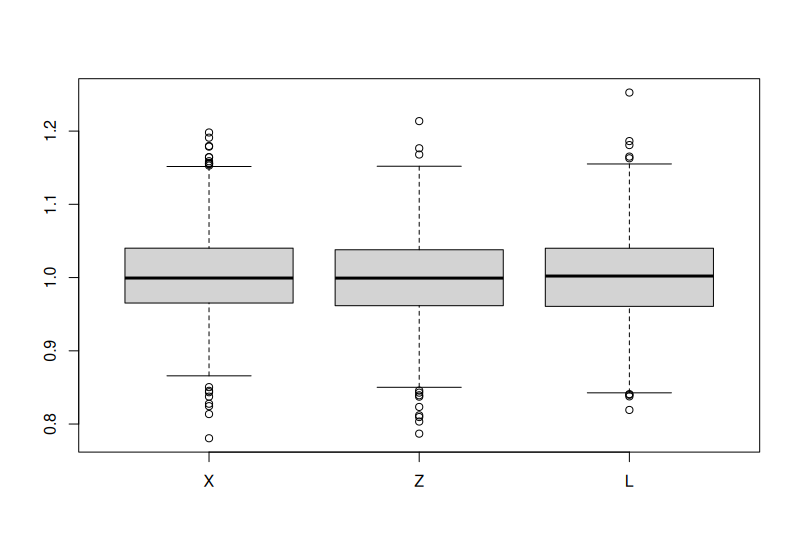
BMA with prior inclusion probability of 0.5 for all regressors (a priori models with ~7-8 vars are preferred)
BMA with prior inclusion probability of 0.3 (a priori models with 5 vars are preferred)
Non-collapsibility in BMA??
Posterior means from 1000 simulations:
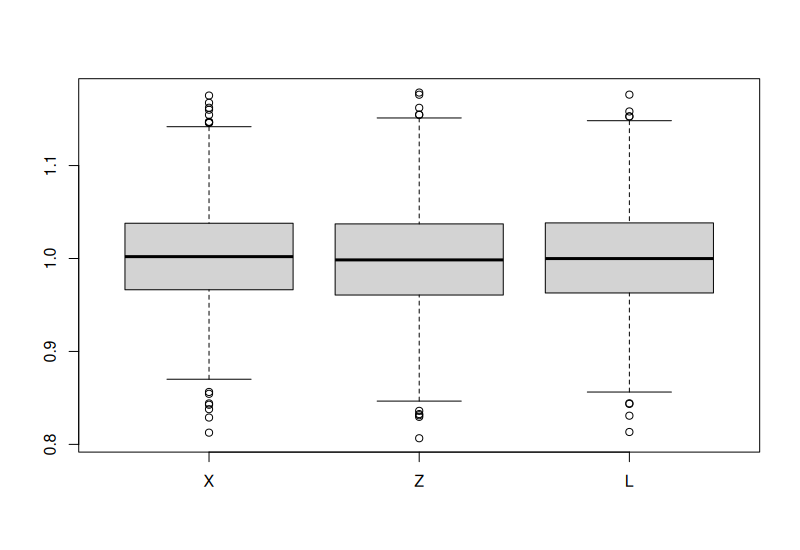
Linear Model BMA
As comparison: \(Y = X + Z + L - L_1 + \epsilon, \quad \epsilon \sim \text{N(0,1)}.\)